
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Yong-ho Lee, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):232-241. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0355
- 3,601 View
- 222 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate whether non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without sarcopenia is associated with progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We investigated 852 T2DM patients who underwent abdominal ultrasonography, bioelectrical impedance analysis, and carotid artery ultrasonography at baseline and repeated carotid ultrasonography after 6 to 8 years. NAFLD was confirmed by abdominal ultrasonography, and sarcopenia was defined as a sex-specific skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) value <2 standard deviations below the mean for healthy young adults. SMI was calculated by dividing the sum of appendicular skeletal mass by body weight. We investigated the association between NAFLD with or without sarcopenia and the progression of carotid atherosclerosis.
Results
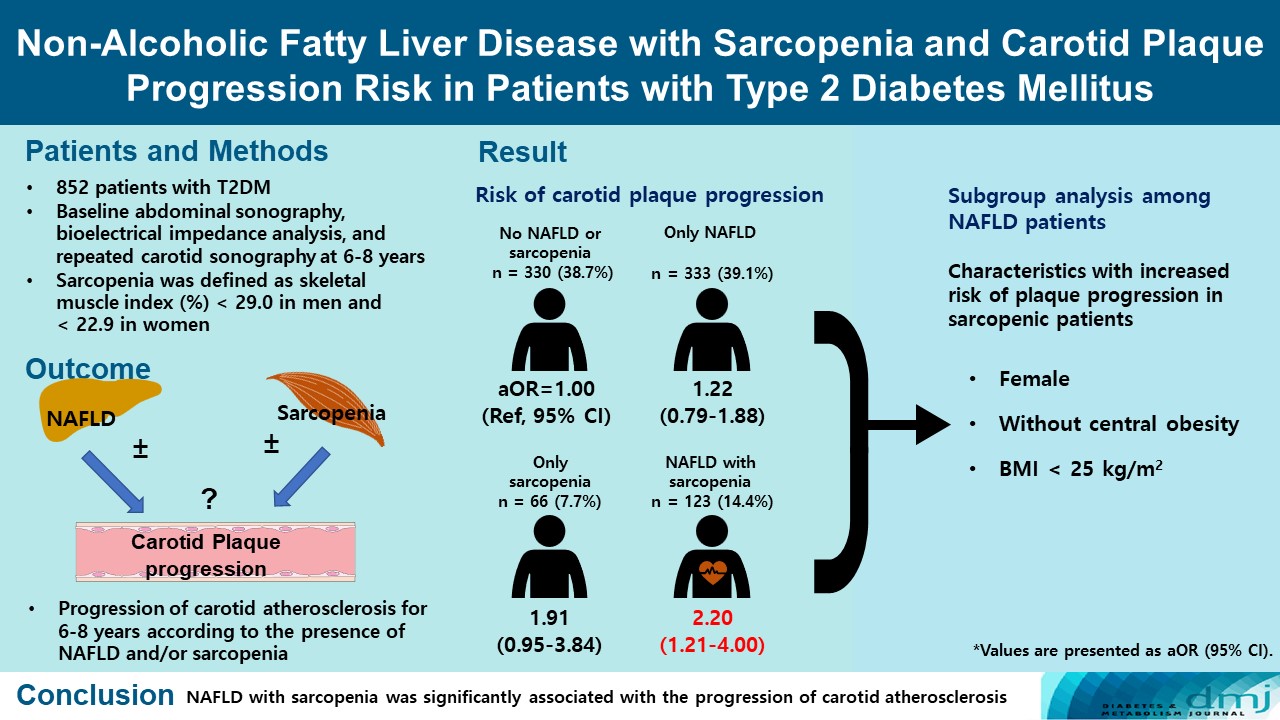
Of the 852 patients, 333 (39.1%) were classified as NAFLD without sarcopenia, 66 (7.7%) were classified as sarcopenia without NAFLD, and 123 (14.4%) had NAFLD with sarcopenia at baseline. After 6 to 8 years, patients with both NAFLD and sarcopenia had a higher risk of atherosclerosis progression (adjusted odds ratio, 2.20; P<0.009) than controls without NAFLD and sarcopenia. When a subgroup analysis was performed on only patients with NAFLD, female sex, absence of central obesity, and non-obesity were significant factors related to increased risk of plaque progression risk in sarcopenic patients.
Conclusion
NAFLD with sarcopenia was significantly associated with the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
Aditya Viswanath, Sherouk Fouda, Cornelius James Fernandez, Joseph M Pappachan
World Journal of Hepatology.2024; 16(2): 152. CrossRef - Prevalence and outcome of sarcopenia in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Suprabhat Giri, Prajna Anirvan, Sumaswi Angadi, Ankita Singh, Anurag Lavekar
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and carotid media‐intima thickness: A systematic review and a meta‐analysis
Manouchehr Khoshbaten, Sepideh H. Maleki, Sara Hadad, Amrit Baral, Ana V. Rocha, Laxmi Poudel, Alireza Abdshah
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes and sarcopenia
Yu. G. Samoilova, M. V. Matveeva, E. A. Khoroshunova, D. V. Podchinenova, L. L. Maksimova, G. G. Gorbach, A. B. Trivozhenko, V. A. Avkhimenko
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2023; 23(1): 3655. CrossRef
- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
- Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:630-9)
- Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):956-957. Published online November 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0381
- [Original]
- 1,663 View
- 101 Download
- Complications
- Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Da Hea Seo, Young Ju Suh, Yongin Cho, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongha Seo, Seongbin Hong, Yong-ho Lee, Young Ju Choi, Eunjig Lee, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):630-639. Published online January 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0130
- 5,528 View
- 274 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, the causal relationship between NAFLD and CKD is uncertain, particularly in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We aimed to investigate the association between the presence and severity of NAFLD and incident CKD in patients with T2DM.
Methods
In this longitudinal cohort study of patients with T2DM, 3,188 patients with preserved renal function were followed up for the occurrence of incident CKD. NAFLD was defined as the presence of hepatic steatosis on ultrasonography, without any other causes of chronic liver disease. Advanced liver fibrosis of NAFLD was defined as a fibrosis-4 index ≥2.67. CKD was defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Results
At baseline, 1,729 (54.2%) patients had NAFLD, of whom 94 (5.4%) had advanced liver fibrosis. During the follow-up of 8.3±3.6 years, 472 (14.8%) patients developed incident CKD: 220 (15.1%) in the non-NAFLD group, 231 (14.1%) in the NAFLD without advanced fibrosis group and 28 (31.1%) in the NAFLD with advanced fibrosis group. There was no increased risk of incident CKD in the NAFLD group compared to the non-NAFLD group (P=0.435). However, among patients with NAFLD, advanced liver fibrosis was associated with an increased risk of CKD (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.75; 95% confidence interval, 1.15 to 2.66; P=0.009).
Conclusion
Advanced liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD is independently associated with an increased risk of incident CKD in patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Esteatosis hepática metabólica y nefropatía diabética: una llamada a la acción
Salvador Benlloch, Francesc Moncho, Jose Luis Górriz
Nefrología.2024; 44(2): 129. CrossRef - Longitudinal Outcomes Associated With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Meta-analysis of 129 Studies
Kai En Chan, Elden Yen Hng Ong, Charlotte Hui Chung, Christen En Ya Ong, Benjamin Koh, Darren Jun Hao Tan, Wen Hui Lim, Jie Ning Yong, Jieling Xiao, Zhen Yu Wong, Nicholas Syn, Apichat Kaewdech, Margaret Teng, Jiong-Wei Wang, Nicholas Chew, Dan Yock Young
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2024; 22(3): 488. CrossRef - Association of NAFLD/NASH, and MAFLD/MASLD with chronic kidney disease: an updated narrative review
Amedeo Lonardo
Metabolism and Target Organ Damage.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in diabetic kidney disease: A call to action
Salvador Benlloch, Francesc Moncho, Jose Luis Górriz
Nefrología (English Edition).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - MAFLD and NAFLD in the prediction of incident chronic kidney disease
So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Janghyun Koh, Jae Hwan Jee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Mira Kang, Sang-Man Jin
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of non-invasive indices of liver steatosis and fibrosis with progressive kidney impairment in adults with type 2 diabetes
Mei Chung Moh, Sharon Li Ting Pek, Kenny Ching Pan Sze, Serena Low, Tavintharan Subramaniam, Keven Ang, Wern Ee Tang, Simon Biing Ming Lee, Chee Fang Sum, Su Chi Lim
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(6): 827. CrossRef - Pancreatic beta-cell specific BAG3 knockout results in chronic hyperinsulinemia inducing insulin resistance
Verena Damiani, Alessia Lamolinara, Ilaria Cicalini, Maria Concetta Cufaro, Francesco Del Pizzo, Federica Di Marco, Piero Del Boccio, Beatrice Dufrusine, Michael Hahne, Rossano Lattanzio, Damiana Pieragostino, Manuela Iezzi, Massimo Federici, Maria Cateri
Molecular Metabolism.2023; 74: 101752. CrossRef - Utility of non-invasive liver fibrosis markers to predict the incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD): A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Rudi Supriyadi, Theo Audi Yanto, Timotius Ivan Hariyanto, Ketut Suastika
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102814. CrossRef - Significance of Diabetic Kidney Disease Biomarkers in Predicting Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jaehyun Bae, Byung-Wan Lee
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1928. CrossRef - Hepatic Fibrosis Evaluated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes with and without Chronic Kidney Disease
Therese Adrian, Mads Hornum, Filip Krag Knop, Karl Bang Christensen, Thomas Almdal, Peter Rossing, Lisa Í Lídaa, Niels Søndergaard Heinrich, Vincent Oltman Boer, Anouk Marsman, Esben Thade Petersen, Hartwig Roman Siebner, Bo Feldt-Rasmussen
Nephron.2023; 147(11): 673. CrossRef - Clinical Interest of Serum Alpha-2 Macroglobulin, Apolipoprotein A1, and Haptoglobin in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, with and without Type 2 Diabetes, before or during COVID-19
Olivier Deckmyn, Thierry Poynard, Pierre Bedossa, Valérie Paradis, Valentina Peta, Raluca Pais, Vlad Ratziu, Dominique Thabut, Angelique Brzustowski, Jean-François Gautier, Patrice Cacoub, Dominique Valla
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 699. CrossRef - Fibrosis Risk in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Related to Chronic Kidney Disease in Older Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Yifan Sun, Liang Hong, Zhe Huang, Lihong Wang, Yanqin Xiong, Shuhang Zong, Rui Zhang, Jun Liu, Shufei Zang
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): e3661. CrossRef - Beyond Liver Disease: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Kidney Disease
Eugene Han
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 564. CrossRef - A higher FIB‐4 index is associated with an increased incidence of renal failure in the general population
Eva Maria Schleicher, Simon Johannes Gairing, Peter Robert Galle, Julia Weinmann‐Menke, Jörn M. Schattenberg, Karel Kostev, Christian Labenz
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(12): 3505. CrossRef - Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:630-9)
Ji Hye Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 953. CrossRef - Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:630-9)
Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 956. CrossRef
- Esteatosis hepática metabólica y nefropatía diabética: una llamada a la acción
- Complications
- Serum Levels of Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Are Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Preserved Renal Function
- Da Hea Seo, Moonsuk Nam, Mihye Jung, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):875-886. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0221
- 5,623 View
- 123 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Recent studies have demonstrated that the levels of adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP) are closely associated with diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to examine the association between serum A-FABP level and rapid renal function decline in patients with T2DM and preserved renal function.
Methods This was a prospective observational study of 452 patients with T2DM and preserved renal function who had serial measurements of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Rapid renal function decline was defined as an eGFR decline of >4% per year. The association between baseline serum A-FABP level and rapid renal function decline was investigated.
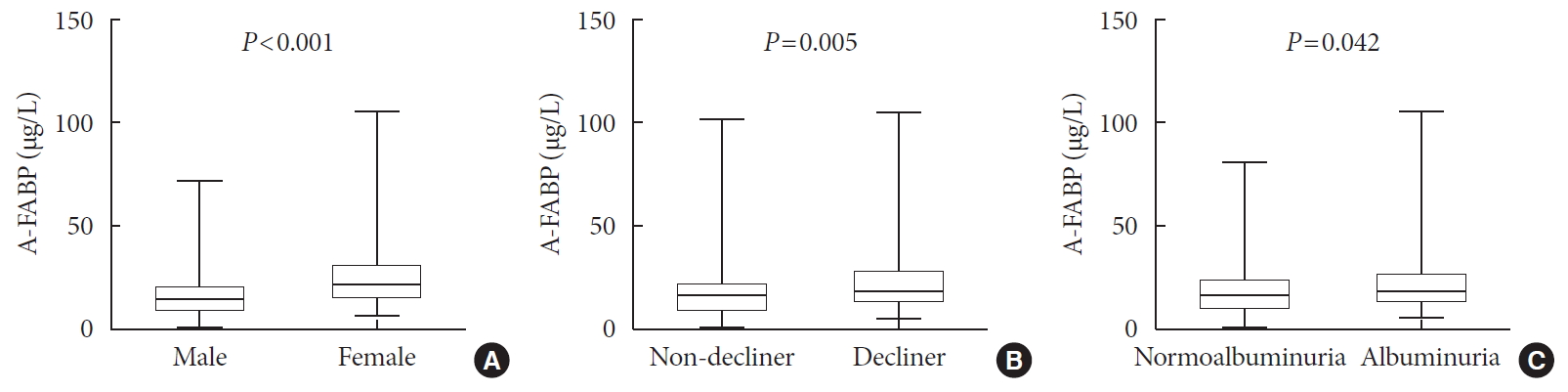
Results Over a median follow-up of 7 years, 82 participants (18.1%) experienced rapid renal function decline. Median A-FABP levels were significantly higher in patients with rapid renal function decline, compared to non-decliners (20.2 ng/mL vs. 17.2 ng/mL,
P =0.005). A higher baseline level of A-FABP was associated with a greater risk of developing rapid renal function decline, independent of age, sex, duration of diabetes, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, history of cardiovascular disease, baseline eGFR, urine albumin creatinine ratio, total cholesterol, glycosylated hemoglobin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of thiazolidinedione, insulin, angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II-receptor blockers and statin (odds ratio, 3.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.53 to 6.29;P =0.002).Conclusion A high level of serum A-FABP is associated with an increased risk of rapid renal function decline in patients with T2DM and preserved renal function. This suggests that A-FABP could play a role in the progression of DKD in the early stages.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 as a biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes
Amr M. Shaker, Maggie E. Mohamed, Tarek Ramzy, Mayssa I. Ali
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating thrombospondin-2 level for identifying individuals with rapidly declining kidney function trajectory in type 2 diabetes: a prospective study of the Hong Kong West Diabetes Registry
Chi-Ho Lee, David Tak-Wai Lui, Chloe Yu-Yan Cheung, Carol Ho-Yi Fong, Michele Mae-Ann Yuen, Wing-Sun Chow, Aimin Xu, Karen Siu-Ling Lam
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of inflammatory cytokines and estimated glomerular filtration rate decline in Japanese patients with diabetic kidney disease: a pilot study
Yuka Sugawara, Yosuke Hirakawa, Koki Mise, Kosuke Kashiwabara, Ko Hanai, Satoshi Yamaguchi, Akihiro Katayama, Yasuhiro Onishi, Yui Yoshida, Naoki Kashihara, Yutaka Matsuyama, Tetsuya Babazono, Masaomi Nangaku, Jun Wada
Biomarkers in Medicine.2022; 16(10): 759. CrossRef - The role of statins in patients with early diabetic nephropathy
Xi Zhao, Shu Chun Zhou, Xiu Fang Wang, Hong Wu Liao
Medicine.2022; 101(24): e29099. CrossRef - Serum Adipocyte Fatty-Acid Binding Protein as an Independent Marker of Peripheral Artery Disease in Patients with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bang-Gee Hsu, Chin-Yee Mah, Du-An Wu, Ming-Chun Chen
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(15): 9459. CrossRef - Fatty acid-binding protein 4 in kidney diseases: From mechanisms to clinics
Weijing Lai, Min Shi, Rongshuang Huang, Ping Fu, Liang Ma
European Journal of Pharmacology.2022; 931: 175224. CrossRef - Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels and responses of pancreatic islet β-cells and α-cells in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hong Wang, Jie Cao, Jian-bin Su, Xue-qin Wang, Xing Wang, Dong-mei Zhang, Xiao-hua Wang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Low-Expression Variant of FABP4 Is Associated With Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes
Emma H. Dahlström, Jani Saksi, Carol Forsblom, Nicoline Uglebjerg, Nina Mars, Lena M. Thorn, Valma Harjutsalo, Peter Rossing, Tarunveer S. Ahluwalia, Perttu J. Lindsberg, Niina Sandholm, Per-Henrik Groop
Diabetes.2021; 70(10): 2391. CrossRef - White adipocyte-targeted dual gene silencing of FABP4/5 for anti-obesity, anti-inflammation and reversal of insulin resistance: Efficacy and comparison of administration routes
Jee Young Chung, Juhyeong Hong, Hyung-Jin Kim, Yoonsung Song, Seok-Beom Yong, Jieun Lee, Yong-Hee Kim
Biomaterials.2021; 279: 121209. CrossRef
- Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 as a biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes
- Response: Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function (
Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:840–53) - Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Moonsuk Nam
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):205-206. Published online February 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0025
- [Original]
- 2,878 View
- 57 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial DNA and Inflammation Are Associated with Cerebral Vessel Remodeling and Early Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ligia Petrica, Florica Gadalean, Danina Mirela Muntean, Dragos Catalin Jianu, Daliborca Vlad, Victor Dumitrascu, Flaviu Bob, Oana Milas, Anca Suteanu-Simulescu, Mihaela Glavan, Sorin Ursoniu, Lavinia Balint, Maria Mogos-Stefan, Silvia Ienciu, Octavian Mar
Biomolecules.2024; 14(4): 499. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial DNA and Inflammation Are Associated with Cerebral Vessel Remodeling and Early Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients Treated with Statins for Residual Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
- Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jae Myung Yu, Sung Rae Kim, In Kye Lee, Kyung-Ah Han, Sung Hee Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Ji-Oh Mok, Yong-ho Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, So Hun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Ah Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Sung-Ho Her, Won Yong Shin, Mi-Seung Shin, Hyo-Suk Ahn, Seung Ho Kang, Jin-Man Cho, Sang-Ho Jo, Tae-Joon Cha, Seok Yeon Kim, Kyung Heon Won, Dong-Bin Kim, Jae Hyuk Lee, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):78-90. Published online June 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0265
- 9,266 View
- 189 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Cardiovascular risk remains increased despite optimal low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level induced by intensive statin therapy. Therefore, recent guidelines recommend non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) as a secondary target for preventing cardiovascular events. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and tolerability of omega-3 fatty acids (OM3-FAs) in combination with atorvastatin compared to atorvastatin alone in patients with mixed dyslipidemia.
Methods This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, and phase III multicenter study included adults with fasting triglyceride (TG) levels ≥200 and <500 mg/dL and LDL-C levels <110 mg/dL. Eligible subjects were randomized to ATOMEGA (OM3-FAs 4,000 mg plus atorvastatin calcium 20 mg) or atorvastatin 20 mg plus placebo groups. The primary efficacy endpoints were the percent changes in TG and non-HDL-C levels from baseline at the end of treatment.
Results After 8 weeks of treatment, the percent changes from baseline in TG (−29.8% vs. 3.6%,
P <0.001) and non-HDL-C (−10.1% vs. 4.9%,P <0.001) levels were significantly greater in the ATOMEGA group (n =97) than in the atorvastatin group (n =103). Moreover, the proportion of total subjects reaching TG target of <200 mg/dL in the ATOMEGA group was significantly higher than that in the atorvastatin group (62.9% vs. 22.3%,P <0.001). The incidence of adverse events did not differ between the two groups.Conclusion The addition of OM3-FAs to atorvastatin improved TG and non-HDL-C levels to a significant extent compared to atorvastatin alone in subjects with residual hypertriglyceridemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between Omega‐3 Fatty Acid Intake and Dyslipidemia: A Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Tianjiao Wang, Xin Zhang, Na Zhou, Yuxuan Shen, Biao Li, Bingshu E. Chen, Xinzhi Li
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutraceutical support in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
E. V. Gracheva, E. A. Starovoytova, E. S. Kulikov, N. A. Kirillova, S. V. Fedosenko, M. A. Balaganskaya, D. V. Kromka
Rational Pharmacotherapy in Cardiology.2023; 19(3): 298. CrossRef - Effect of coadministration of omega-3 fatty acids with glimepiride on glycemic control, lipid profile, irisin, and sirtuin-1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized controlled trial
Rehab H. Werida, Aalaa Ramzy, Youssri Nassief Ebrahim, Maged Wasfy Helmy
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Dietary Interventions on Hypertriglyceridemia: From Public Health to Molecular Nutrition Evidence
Karla Paulina Luna-Castillo, Xochitl Citlalli Olivares-Ochoa, Rocío Guadalupe Hernández-Ruiz, Iris Monserrat Llamas-Covarrubias, Saraí Citlalic Rodríguez-Reyes, Alejandra Betancourt-Núñez, Barbara Vizmanos, Erika Martínez-López, José Francisco Muñoz-Valle
Nutrients.2022; 14(5): 1104. CrossRef - The effect of omega-3 fatty acids and its combination with statins on lipid profile in patients with hypertriglyceridemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yunjiao Yang, Wen Deng, Yanmei Wang, Tongyi Li, Yiding Chen, Cong Long, Qing Wen, Yue Wu, Qiu Chen
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Atorvastatin 40 mg/ω-3 Fatty Acids 4 g Fixed-dose Combination and Atorvastatin 40 mg Monotherapy in Hypertriglyceridemic Patients who Poorly Respond to Atorvastatin 40 mg Monotherapy: An 8-week, Multicenter, Random
Jong Shin Woo, Soon Jun Hong, Dong Hoon Cha, Kee Sik Kim, Moo Hyun Kim, Jun-Won Lee, Myung Ho Jeong, Jin-Ok Jeong, Jun-Hee Lee, Doo Soo Jeon, Eun Joo Cho, Soon Kil Kim, Jun Kwan, Chang Gyu Park, Hae Young Lee, Taek Jong Hong, Jinho Shin, Ho Joong Youn, Do
Clinical Therapeutics.2021; 43(8): 1419. CrossRef - All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Death between Statins and Omega-3 Supplementation: A Meta-Analysis and Network Meta-Analysis from 55 Randomized Controlled Trials
Jeongseon Kim, Tung Hoang, Ji-Myung Kim, So Young Bu, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Eunju Park, Seung-Min Lee, Eunmi Park, Ji Yeon Min, In Seok Lee, So Young Youn, Jee-Young Yeon
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 3203. CrossRef
- Association Between Omega‐3 Fatty Acid Intake and Dyslipidemia: A Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Complications
- Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function
- Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Joon Ho Song, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim, Moonsuk Nam
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):840-853. Published online March 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0186
- 5,521 View
- 57 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Recent evidences indicate that early rapid renal function decline is closely associated with the development and progression of diabetic kidney disease. We have investigated the association between carotid atherosclerosis and rapid renal function decline in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and preserved renal function.
Methods In a prospective, multicenter cohort, a total of 967 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and preserved renal function were followed for 6 years with serial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) measurements. Common carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and presence of carotid plaque were assessed at baseline. Rapid renal function decline was defined as an eGFR decline >3.3% per year.
Results Over a median follow-up of 6 years, 158 participants (16.3%) developed rapid renal function decline. While there was no difference in CIMT, the presence of carotid plaque in rapid decliners was significantly higher than in non-decliners (23.2% vs. 12.2%,
P <0.001). In multivariable logistic regression analysis, presence of carotid plaque was an independent predictor of rapid renal function decline (odds ratio, 2.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.48 to 3.68;P <0.0001) after adjustment for established risk factors. The model including the carotid plaque had better performance for discrimination of rapid renal function decline than the model without carotid plaque (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve 0.772 vs. 0.744,P =0.016).Conclusion Close monitoring of renal function and early intensive management may be beneficial in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and carotid plaques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation analysis of carotid plaque in young patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio
Huijun Wen, Hai Yu
Vascular.2023; 31(1): 90. CrossRef - Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
Yiwen Li, Yanfei Liu, Shiwei Liu, Mengqi Gao, Wenting Wang, Keji Chen, Luqi Huang, Yue Liu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Carotid intima-media thickness and atherosclerotic plaques are associated with renal function decline: a 14-year longitudinal population-based study
Miriam Goepfert, Till Ittermann, Marcus Dörr, Nele Friedrich, Henry Völzke, Thomas Dabers, Stephan B Felix, Ulf Schminke, Sylvia Stracke, Sabrina von Rheinbaben
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023; 38(11): 2598. CrossRef - Blood pressure and vascular determinants of glomerular filtration rate decline in diabetic kidney disease
Luca Truscello, Dina Nobre, Vehashini Sabaratnam, Olivier Bonny, Grégoire Wuerzner, Michel Burnier, Fadi Fakhouri, Menno Pruijm, Anne Zanchi
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Explainable Artificial Intelligence Paves the Way in Precision Diagnostics and Biomarker Discovery for the Subclass of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetics
Fatma Hilal Yagin, Seyma Yasar, Yasin Gormez, Burak Yagin, Abdulvahap Pinar, Abedalrhman Alkhateeb, Luca Paolo Ardigò
Metabolites.2023; 13(12): 1204. CrossRef - Evaluation of Subclinical Vascular Disease in Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Tool for Personalization of Management of a High-Risk Population
Christodoula Kourtidou, Vasileios Rafailidis, Garyfallia Varouktsi, Efthimios Kanakis, Vassilios Liakopoulos, Timoleon-Achilleas Vyzantiadis, Maria Stangou, Smaragdi Marinaki, Konstantinos Tziomalos
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1139. CrossRef - Prevalence and Predictors of Renal Disease in a National Representative Sample of the Romanian Adult Population: Data from the SEPHAR IV Survey
Călin Pop, Oana Florentina Gheorghe Fronea, Ioana Antonia Branea, Lucian Mihai Itu, Roxana Darabont, Irinel Parepa, Theodora Benedek, Maria Dorobantu
Diagnostics.2022; 12(12): 3199. CrossRef - Clinical features of and risk factors for normoalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Qi Dai, Nan Chen, Ling Zeng, Xin-Jie Lin, Feng-Xiu Jiang, Xiong-Jie Zhuang, Ze-Yuan Lu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictive Value of Carotid Ultrasonography With Cardiovascular Risk Factors—A “SPIDER” Promoting Atherosclerosis
Hongwei Li, Xiaolin Xu, Baoming Luo, Yuling Zhang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on pathogenesis and diagnosis flow of normoalbuminuric diabetes with renal insufficiency
Le Deng, Wenjie Li, Gaosi Xu
European Journal of Medical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum fibroblast growth factor 21 with kidney function in a population-based Chinese cohort
Rui Zhang, Yufeng Li, Xianghai Zhou, Fang Zhang, Meng Li, Simin Zhang, Xiuying Zhang, Xin Wen, Linong Ji
Medicine.2021; 100(50): e28238. CrossRef - Letter: Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:840–53)
Min-Ji Kim, Jae-Han Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 201. CrossRef - Response: Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:840–53)
Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Moonsuk Nam
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 205. CrossRef - Serum Levels of Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Are Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Preserved Renal Function
Da Hea Seo, Moonsuk Nam, Mihye Jung, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 875. CrossRef - Proteinuria Is Associated with Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Non-Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jaehyun Bae, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 136. CrossRef
- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Clinical Care/Education
- Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Health Behaviors, Metabolic Control, and Chronic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- So Hun Kim, Seung Youn Lee, Chei Won Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seongbin Hong, Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hae Seo, Moon-Suk Nam, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):380-393. Published online June 29, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0102
- 4,826 View
- 67 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of the study was to assess the impact of socioeconomic status (SES) on health behaviors, metabolic control, and chronic complications in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from South Korea, a country with universal health insurance coverage and that has experienced rapid economic and social transition.
Methods A total of 3,294 Korean men and women with T2DM aged 30 to 65 years, participating in the Korean National Diabetes Program (KNDP) cohort who reported their SES and had baseline clinical evaluation were included in the current cross-sectional analysis. SES included the level of education and monthly household income.
Results Lower education level and lower income level were closely related, and both were associated with older age in men and women. Women and men with lower income and education level had higher carbohydrate and lower fat intake. After adjustment for possible confounding factors, higher education in men significantly lowered the odds of having uncontrolled hyperglycemia (glycosylated hemoglobin ≥7.5%) (odds ratio [OR], 0.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.43 to 0.91 for highest education;
P trend=0.048), while higher household income in men significantly lowered the odds of having diabetic retinopathy (OR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.95 for highest income level;P trend=0.048). In women, lower income was associated with a higher stress level.Conclusion Men with lower SES had higher odds of having diabetic retinopathy and uncontrolled hyperglycemia, showing the need to improve care targeted to this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Scoping Review of Possible Solutions for Decreasing Socioeconomic Inequalities in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Laleh Gharacheh, Mostafa Amini-Rarani, Amin Torabipour, Saeed Karimi
International Journal of Preventive Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Socioeconomic status and the effect of prolonged pandemic confinement on anthropometric and glycaemic outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chandana Wijeweera, Ummul Muhfaza, Reginald V. Lord, Peter Petocz, Juliana Chen, Veronica Preda
Primary Care Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of diet quality with glycemia, insulinemia, and insulin resistance in families at high risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus in Europe: Feel4 Diabetes Study
Botsi E, Karatzi K, Mavrogianni C, Kaloyan Tsochev, Esther M González-Gil, Radó S, Kivelä J, Wikström K, Cardon G, Rurik I, Liatis S, Tsvetalina Tankova, Violeta Iotova, Luis A. Moreno, Makrillakis K, Manios Y, Tsigos C
Nutrition.2023; 105: 111805. CrossRef - Sustained Low Income, Income Changes, and Risk of All-Cause Mortality in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hong Seok Lee, Jimin Clara Park, Inkwan Chung, Junxiu Liu, Seong-Su Lee, Kyungdo Han
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(1): 92. CrossRef - Association of birth weight with risk of diabetes mellitus in adolescence and early adulthood: analysis of the Indonesian Family Life Survey
Ratu Ayu Dewi Sartika, Fathimah Sulistyowati Sigit, Edy Purwanto, Norliyana Aris, Avliya Quratul Marjan, Wahyu Kurnia Yusrin Putra, Sutanto Priyo Hastono
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 267. CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes Quality Assessment on Diabetes Management Behaviors Based on a Nationwide Survey
Chang Kyun Choi, Jungho Yang, Ji-An Jeong, Min-Ho Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15781. CrossRef - FOLLOW-UP ADHERENCE IN PATIENTS WITH NONPROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY PRESENTING TO AN OPHTHALMIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT
Arjun Watane, Meghana Kalavar, Elizabeth A. Vanner, Kara Cavuoto, Jayanth Sridhar
Retina.2021; 41(6): 1293. CrossRef - Socioeconomic disparity in global vision loss burden due to diabetic retinopathy: an analysis on time trends from 1990 to 2017
Yi Shan, Yufeng Xu, Lingxia Ye, Xiling Lin, Yaoyao Chen, Qi Miao, Juan Ye
Endocrine.2021; 73(2): 316. CrossRef - Tip 2 Diyabetli Bireylerin Hastalık Yönetiminde Karşılaştıkları Engellerin Değerlendirilmesi
Şuheda ÜSTÜNDAĞ, Nuray DAYAPOĞLU
Adnan Menderes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 5(3): 514. CrossRef - Socioeconomic inequalities in type 2 diabetes in employed individuals, nonworking spouses and pensioners
Batoul Safieddine, Stefanie Sperlich, Johannes Beller, Karin Lange, Jelena Epping, Juliane Tetzlaff, Fabian Tetzlaff, Siegfried Geyer
SSM - Population Health.2020; 11: 100596. CrossRef - Thirteen-year trends in the prevalence of diabetes according to socioeconomic condition and cardiovascular risk factors in a Swiss population
Carlos de Mestral, Silvia Stringhini, Idris Guessous, François R Jornayvaz
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(1): e001273. CrossRef - Dietary Habits and Dietary Antioxidant Intake Are Related to Socioeconomic Status in Polish Adults: A Nationwide Study
Małgorzata Elżbieta Zujko, Anna Waśkiewicz, Wojciech Drygas, Alicja Cicha-Mikołajczyk, Kinga Zujko, Danuta Szcześniewska, Krystyna Kozakiewicz, Anna Maria Witkowska
Nutrients.2020; 12(2): 518. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
Bo-Yeon Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 487. CrossRef - Gender in Endocrine Diseases: Role of Sex Gonadal Hormones
R. Lauretta, M. Sansone, A. Sansone, F. Romanelli, M. Appetecchia
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef
- A Scoping Review of Possible Solutions for Decreasing Socioeconomic Inequalities in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Beneficial Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training Combined with Rosiglitazone on Glucose Metabolism in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats
- Shan-Ji Piao, So Hun Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seong-Bin Hong, Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hae Seo, In-Sun Park, Moonsuk Nam
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):474-485. Published online November 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.474
- 3,831 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Regular aerobic exercise is essential for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and may be particularly beneficial for those treated with thiazolidinediones, since it may prevent associated weight gain. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of combined exercise and rosiglitazone treatment on body composition and glucose metabolism in obese diabetes-prone animals.
Methods We analyzed metabolic parameters, body composition, and islet profiles in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty rats after 28 weeks of aerobic exercise, rosiglitazone treatment, and combined exercise and rosiglitazone treatment.
Results Combined exercise with rosiglitazone showed significantly less increase in weight and epididymal fat compared to rosiglitazone treatment. Aerobic exercise alone and combined rosiglitazone and exercise treatment led to similar retention of lean body mass. All experimental groups showed a decrease in fasting glucose. However, the combined exercise and rosiglitazone therapy group showed prominent improvement in glucose tolerance compared to the other groups. Rescue of islet destruction was observed in all experimental groups, but was most prominent in the combined therapy group.
Conclusion Regular aerobic exercise combined with rosiglitazone treatment can compensate for the adverse effect of rosiglitazone treatment and has benefit for islet preservation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impacts of an Exercise Intervention on the Health of Pancreatic Beta-Cells: A Review
Shuang Zhang, Yaru Wei, Chunxiao Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(12): 7229. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms by which aerobic exercise induces insulin sensitivity
Habib Yaribeygi, Stephen L. Atkin, Luis E. Simental‐Mendía, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(8): 12385. CrossRef
- Impacts of an Exercise Intervention on the Health of Pancreatic Beta-Cells: A Review
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Brown Fat and Browning for the Treatment of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders
- So Hun Kim, Jorge Plutzky
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(1):12-21. Published online January 21, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.1.12
- 7,430 View
- 110 Download
- 155 Web of Science
- 158 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Brown fat is a specialized fat depot that can increase energy expenditure and produce heat. After the recent discovery of the presence of active brown fat in human adults and novel transcription factors controlling brown adipocyte differentiation, the field of the study of brown fat has gained great interest and is rapidly growing. Brown fat expansion and/or activation results in increased energy expenditure and a negative energy balance in mice and limits weight gain. Brown fat is also able to utilize blood glucose and lipid and results in improved glucose metabolism and blood lipid independent of weight loss. Prolonged cold exposure and beta adrenergic agonists can induce browning of white adipose tissue. The inducible brown adipocyte, beige adipocyte evolving by thermogenic activation of white adipose tissue have different origin and molecular signature from classical brown adipocytes but share the characteristics of high mitochondria content, UCP1 expression and thermogenic capacity when activated. Increasing browning may also be an efficient way to increase whole brown fat activity. Recent human studies have shown possibilities that findings in mice can be reproduced in human, making brown fat a good candidate organ to treat obesity and its related disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modulation of angiogenic switch in reprogramming browning and lipid metabolism in white adipocytes
Sreelekshmi Sreekumar, Karyath Palliyath Gangaraj, Manikantan Syamala Kiran
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids.2024; 1869(1): 159423. CrossRef - Anti-Obesity Effects of GABA in C57BL/6J Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Heegu Jin, Hyein Han, Gunju Song, Hyun-Ji Oh, Boo-Yong Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 995. CrossRef - Citrus aurantium L. and synephrine improve brown adipose tissue function in adolescent mice programmed by early postnatal overfeeding
Andressa Cardoso Guimarães, Egberto Gaspar de Moura, Stephanie Giannini Silva, Bruna Pereira Lopes, Iala Milene Bertasso, Carla Bruna Pietrobon, Fernanda Torres Quitete, Tayanne de Oliveira Malafaia, Érica Patrícia Garcia Souza, Patrícia Cristina Lisboa,
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Au@16-pH-16/miR-21 mimic nanosystem: An efficient treatment for obesity through browning and thermogenesis induction
Said Lhamyani, Adriana-Mariel Gentile, María Mengual-Mesa, Elia Grueso, Rosa M. Giráldez-Pérez, José Carlos Fernandez-Garcia, Antonio Vega-Rioja, Mercedes Clemente-Postigo, John R. Pearson, Isabel González-Mariscal, Gabriel Olveira, Francisco-Javier Bermu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 171: 116104. CrossRef - Walnut supplementation increases levels of UCP1 and CD36 in brown adipose tissue independently of diet type
Tamara Dakic, Dusan Jeremic, Iva Lakic, Nebojsa Jasnic, Aleksandra Ruzicic, Predrag Vujovic, Tanja Jevdjovic
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of micro‐RNAs associated with adipose‐derived extracellular vesicles in metabolic disorders
Thomas Payet, Elisa Gabinaud, Jean‐François Landrier, Lourdes Mounien
Obesity Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Spexin ameliorated obesity-related metabolic disorders through promoting white adipose browning mediated by JAK2-STAT3 pathway
Bihe Zeng, Qin Shen, Bo Wang, Xuan Tang, Jiaqi Jiang, Yiming Zheng, Hongbiao Huang, Wenyu Zhuo, Wang Wang, Yang Gao, Xuan Li, Shuhui Wang, Wenjie Li, Guanghui Qian, Jie Qin, Miao Hou, Haitao Lv
Nutrition & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Newly Synbiotic Combination Alleviates Obesity by Modulating the Gut Microbiota–Fat Axis and Inhibiting the Hepatic TLR4/NF‐κB Signaling Pathway
Yongbo Kang, Peng Ren, Xiaorong Shen, Xiaoyu Kuang, Xiaodan Yang, Haixia Liu, Huan Yan, Hao Yang, Xing Kang, Zeyuan Ding, Xuguang Luo, Jieqiong Ma, Ying Yang, Weiping Fan
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lacticaseibacillus paracasei AO356 ameliorates obesity by regulating adipogenesis and thermogenesis in C57BL/6J male mice
Young In Kim, Eun-Sook Lee, Eun-Ji Song, Dong-Uk Shin, Ji-Eun Eom, Hee Soon Shin, Jung Eun Kim, Ju Yeoun Oh, Young-Do Nam, So-Young Lee
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 101: 105404. CrossRef - Effects of caffeoylquinic acid analogs derived from aerial parts of Artemisia iwayomogi on adipogenesis
Su-Young Han, Jisu Kim, Bo Kyeong Kim, Wan Kyunn Whang, Hyeyoung Min
Food Science and Biotechnology.2023; 32(9): 1215. CrossRef - Anti-obesity effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SKO-001 in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
Mi Jin Choi, Hana Yu, Jea Il Kim, Hee Seo, Ju Gyeong Kim, Seul-Ki Kim, Hak Sung Lee, Hyae Gyeong Cheon
European Journal of Nutrition.2023; 62(4): 1611. CrossRef - Meteorin-like Protein and Asprosin Levels in Children and Adolescents with Obesity and Their Relationship with Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome
Nariman Moradi, Reza Fadaei, Maryam Roozbehkia, Mitra Nourbakhsh, Mona Nourbakhsh, Maryam Razzaghy-Azar, Bagher Larijani
Laboratory Medicine.2023; 54(5): 457. CrossRef - A Novel Mix of Polyphenols and Micronutrients Reduces Adipogenesis and Promotes White Adipose Tissue Browning via UCP1 Expression and AMPK Activation
Francesca Pacifici, Gina Malatesta, Caterina Mammi, Donatella Pastore, Vincenzo Marzolla, Camillo Ricordi, Francesca Chiereghin, Marco Infante, Giulia Donadel, Francesco Curcio, Annalisa Noce, Valentina Rovella, Davide Lauro, Manfredi Tesauro, Nicola Di D
Cells.2023; 12(5): 714. CrossRef - Thromboxane A2-TP axis promotes adipose tissue macrophages M1 polarization leading to insulin resistance in obesity
Ruijie Xu, Yufeng Dai, Xu Zheng, Yongheng Yan, Zhao He, Hao Zhang, Haitao Li, Wei Chen
Biochemical Pharmacology.2023; 210: 115465. CrossRef - Green Tea Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits Preadipocyte Growth via the microRNA‐let‐7a/HMGA2 Signaling Pathway
Wen‐Ting Chen, Meei‐Ju Yang, Yi‐Wei Tsuei, Tsung‐Chen Su, An‐Ci Siao, Yow‐Chii Kuo, Ling‐Ru Huang, Yi Chen, Sy‐Jou Chen, Po‐Chuan Chen, Ching‐Feng Cheng, Hui‐Chen Ku, Yung‐Hsi Kao
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Role and Potential of Polymeric Biomaterials in Clinical Obesity Treatment
Rui-Chian Tang, I-Hsuan Yang, Feng-Huei Lin
Biomacromolecules.2023; 24(8): 3438. CrossRef - Short-duration cold exposure decreases fasting-induced glucose intolerance but has no effect on resting energy expenditure
Rima Solianik, Katerina Židonienė, Marius Brazaitis
Cryobiology.2023; 113: 104564. CrossRef - Caffeine promotes the production of Irisin in muscles and thus facilitates the browning of white adipose tissue
Chang Liu, Yi Li, Ge Song, Xuehan Li, Songyue Chen, Dixin Zou, Huixin Li, Chengyi Hu, Haotian Zhao, Yi Yan
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 108: 105702. CrossRef - Thermogenic Modulation of Adipose Depots: A Perspective on Possible Therapeutic Intervention with Early Cardiorenal Complications of Metabolic Impairment
Ahmed F. El-Yazbi, Mohamed A. Elrewiny, Hosam M. Habib, Ali H. Eid, Perihan A. Elzahhar, Ahmed S.F. Belal
Molecular Pharmacology.2023; 104(5): 187. CrossRef - Rabbit Meat Extract Induces Browning in 3T3−L1 Adipocytes via the AMP−Activated Protein Kinase Pathway
In-Seon Bae, Jeong Ah Lee, Soo-Hyun Cho, Hyoun-Wook Kim, Yunseok Kim, Kangmin Seo, Hyun-Woo Cho, Min Young Lee, Ju Lan Chun, Ki Hyun Kim
Foods.2023; 12(19): 3671. CrossRef - Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—Its Pathophysiology, Association with Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease, and Treatments
Hidekatsu Yanai, Hiroki Adachi, Mariko Hakoshima, Sakura Iida, Hisayuki Katsuyama
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(20): 15473. CrossRef - Brown Fat and Nutrition: Implications for Nutritional Interventions
Lloyd Noriega, Cheng-Ying Yang, Chih-Hao Wang
Nutrients.2023; 15(18): 4072. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review from the Oxidative Stress to the Management of Related Diseases
Giovanni Martemucci, Giuseppe Fracchiolla, Marilena Muraglia, Roberta Tardugno, Roberta Savina Dibenedetto, Angela Gabriella D’Alessandro
Antioxidants.2023; 12(12): 2091. CrossRef - Metabolic responses of light and taste receptors – unexpected actions of GPCRs in adipocytes
Onyinye Nuella Ekechukwu, Mark Christian
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2022; 23(1): 111. CrossRef - The ATF3 inducer protects against diet-induced obesity via suppressing adipocyte adipogenesis and promoting lipolysis and browning
Hui-Chen Ku, Tsai-Yun Chan, Jia-Fang Chung, Yung-Hsi Kao, Ching-Feng Cheng
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 145: 112440. CrossRef - Prednisone stimulates white adipocyte browning via β3-AR/p38 MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
Sulagna Mukherjee, Jong Won Yun
Life Sciences.2022; 288: 120204. CrossRef - Tangeretin prevents obesity by modulating systemic inflammation, fat browning, and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice
Qiyang Chen, Dan Wang, Yue Gu, Zixiao Jiang, Zhiqin Zhou
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2022; 101: 108943. CrossRef - Evaluation of thermal sensitivity is of potential clinical utility for the predictive, preventive, and personalized approach advancing metabolic syndrome management
Sujeong Mun, Kihyun Park, Siwoo Lee
EPMA Journal.2022; 13(1): 125. CrossRef - Effects of a Novel Selective Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α Modulator, Pemafibrate, on Metabolic Parameters: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Hidekatsu Yanai, Hisayuki Katsuyama, Mariko Hakoshima
Biomedicines.2022; 10(2): 401. CrossRef - Historical and cultural aspects of obesity: From a symbol of wealth and prosperity to the epidemic of the 21st century
Marta Sumińska, Rafał Podgórski, Klaudia Bogusz‐Górna, Bogda Skowrońska, Artur Mazur, Marta Fichna
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Biological and Clinical Understanding of the Statin Residual Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha Agonists and Ezetimibe for Its Treatment
Hidekatsu Yanai, Hiroki Adachi, Mariko Hakoshima, Hisayuki Katsuyama
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 3418. CrossRef - Pep19 Has a Positive Effect on Insulin Sensitivity and Ameliorates Both Hepatic and Adipose Tissue Phenotype of Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Renata Silvério, Robson Barth, Andrea S. Heimann, Patrícia Reckziegel, Gustavo J. dos Santos, Silvana Y. Romero-Zerbo, Francisco J. Bermúdez-Silva, Alex Rafacho, Emer S. Ferro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4082. CrossRef - Thermogenic T cells: a cell therapy for obesity?
Ulf H. Beier, Daniel J. Baker, Joseph A. Baur
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2022; 322(6): C1085. CrossRef - Accumulation of γδ T cells in visceral fat with aging promotes chronic inflammation
Maria E. C. Bruno, Sujata Mukherjee, Whitney L. Powell, Stephanie F. Mori, Franklyn K. Wallace, Beverly K. Balasuriya, Leon C. Su, Arnold J. Stromberg, Donald A. Cohen, Marlene E. Starr
GeroScience.2022; 44(3): 1761. CrossRef - Deletion of GPR30 Drives the Activation of Mitochondrial Uncoupling Respiration to Induce Adipose Thermogenesis in Female Mice
Jing Luo, Yao Wang, Elizabeth Gilbert, Dongmin Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of STAT3 enhances UCP1 expression and mitochondrial function in brown adipocytes
Lini Song, Xi Cao, Wenyi Ji, Lili Zhao, Weili Yang, Ming Lu, Jinkui Yang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2022; 926: 175040. CrossRef - TRPC5 deletion in the central amygdala antagonizes high-fat diet-induced obesity by increasing sympathetic innervation
Huan Ma, Chengkang He, Li Li, Peng Gao, Zongshi Lu, Yingru Hu, Lijuan Wang, Yu Zhao, Tingbing Cao, Yuanting Cui, Hongting Zheng, Gangyi Yang, Zhencheng Yan, Daoyan Liu, Zhiming Zhu
International Journal of Obesity.2022; 46(8): 1544. CrossRef - Adapalene induces adipose browning through the RARβ-p38 MAPK-ATF2 pathway
Na Hyun Lee, Mi Jin Choi, Hana Yu, Jea Il Kim, Hyae Gyeong Cheon
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2022; 45(5): 340. CrossRef - Engineering Functional Vascularized Beige Adipose Tissue from Microvascular Fragments of Models of Healthy and Type II Diabetes Conditions
Francisca M. Acosta, Katerina Stojkova, Jingruo Zhang, Eric Ivan Garcia Huitron, Jean X. Jiang, Christopher R. Rathbone, Eric M. Brey
Journal of Tissue Engineering.2022; 13: 204173142211093. CrossRef - Atractylenolide III from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz promotes the activation of brown and white adipose tissue through SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway
Xin Liu, Yuan Huang, Xu Liang, Qiong Wu, Nan Wang, Li-jun Zhou, Wen-wu Liu, Qun Ma, Bei Hu, Huan Gao, Ya-ling Cui, Xiang Li, Qing-chun Zhao
Phytomedicine.2022; 104: 154289. CrossRef - The pathobiology of perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT), the fourth layer of the blood vessel wall
Cassie Hillock-Watling, Avrum I. Gotlieb
Cardiovascular Pathology.2022; 61: 107459. CrossRef - RNA-Binding Proteins in the Regulation of Adipogenesis and Adipose Function
Pengpeng Zhang, Wenyan Wu, Chaofeng Ma, Chunyu Du, Yueru Huang, Haixia Xu, Cencen Li, Xiaofang Cheng, Ruijie Hao, Yongjie Xu
Cells.2022; 11(15): 2357. CrossRef - The Effect of Swimming Training with Cinnamon Consumption on β3-AR and ERK2 Gene Expression in the Visceral Adipose Tissue of Diabetic Rats
Kianoosh Mohammadi, Ali Khajehlandi, Amin Mohammadi
Gene, Cell and Tissue.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Of mice and men: Considerations on adipose tissue physiology in animal models of obesity and human studies
Ioannis G. Lempesis, Dimitrios Tsilingiris, Junli Liu, Maria Dalamaga
Metabolism Open.2022; 15: 100208. CrossRef - The comparison of the effect of acute moderate and high-intensity exercise on the uncoupling protein -1 secretion
Desiana Merawati, Sugiharto Sugiharto, Adi Pranoto, Olivia Andiana, Prayogi Dwina Angga
Jurnal SPORTIF : Jurnal Penelitian Pembelajaran.2022; 8(2): 201. CrossRef - Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Protect against High-Fat Diet-Induced Morphological and Functional Impairments of Brown Fat in Transgenic Fat-1 Mice
Lei Hao, Yong-Hui Nie, Chih-Yu Chen, Xiang-Yong Li, Kanakaraju Kaliannan, Jing X. Kang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11903. CrossRef - Modulation of hypothalamic AMPK phosphorylation by olanzapine controls energy balance and body weight
Vitor Ferreira, Cintia Folgueira, Maria Guillén, Pablo Zubiaur, Marcos Navares, Assel Sarsenbayeva, Pilar López-Larrubia, Jan W. Eriksson, Maria J. Pereira, Francisco Abad-Santos, Guadalupe Sabio, Patricia Rada, Ángela M. Valverde
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155335. CrossRef - Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L. Moench) prevents obesity by reducing lipid accumulation and increasing white adipose browning in high-fat diet-fed mice
Heegu Jin, Hyun-Ji Oh, Sehaeng Cho, Ok-Hwan Lee, Boo-Yong Lee
Food & Function.2022; 13(22): 11840. CrossRef - Functional Attenuation of UCP1 as the Potential Mechanism for a Thickened Blubber Layer in Cetaceans
Ming Zhou, Tianzhen Wu, Yue Chen, Shixia Xu, Guang Yang, Anne Yoder
Molecular Biology and Evolution.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Brown adipose tissue transplantation as a novel alternative to obesity treatment: a systematic review
Moloud Payab, Mina Abedi, Najmeh Foroughi Heravani, Mahdieh Hadavandkhani, Maryam Arabi, Akram Tayanloo-Beik, Motahareh Sheikh Hosseini, Hadis Gerami, Fateme Khatami, Bagher Larijani, Mohammad Abdollahi, Babak Arjmand
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(1): 109. CrossRef - Corylin reduces obesity and insulin resistance and promotes adipose tissue browning through SIRT-1 and β3-AR activation
Chin-Chuan Chen, Chen-Hsin Kuo, Yann-Lii Leu, Shu-Huei Wang
Pharmacological Research.2021; 164: 105291. CrossRef - Inducible beige adipocytes improve impaired glucose metabolism in interscapular BAT-removal mice
Xiao-Wei Jia, Dong-Liang Fang, Xin-Yi Shi, Tao Lu, Chun Yang, Yan Gao
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids.2021; 1866(3): 158871. CrossRef - NNT‐induced tumor cell “slimming” reverses the pro‐carcinogenesis effect of HIF2a in tumors
Zhiyong Xiong, Wei Xiong, Wen Xiao, Changfei Yuan, Jian Shi, Yu Huang, Cheng Wang, Xiangui Meng, Zhixian Chen, Hongmei Yang, Ke Chen, Xiaoping Zhang
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - CD10 marks non-canonical PPARγ-independent adipocyte maturation and browning potential of adipose-derived stem cells
Smarajit Chakraborty, Wee Kiat Ong, Winifred W. Y. Yau, Zhihong Zhou, K. N. Bhanu Prakash, Sue-Anne Toh, Weiping Han, Paul M. Yen, Shigeki Sugii
Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulatory roles of G-protein coupled receptors in adipose tissue metabolism and their therapeutic potential
Hyeonyeong Im, Ji-Hyun Park, Seowoo Im, Juhyeong Han, Kyungmin Kim, Yun-Hee Lee
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2021; 44(2): 133. CrossRef - 3-N-butylphthalide protects against high-fat-diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice and increases metabolism in lipid-accumulating cells
Kang-Yun Lu, Shinn-Zong Lin, Kingsley Theras Primus Dass, Wei-Ju Lin, Shih-Ping Liu, Horng-Jyh Harn
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 139: 111687. CrossRef - Ellagic acid induces beige remodeling of white adipose tissue by controlling mitochondrial dynamics and SIRT3
Woo Yong Park, Jinbong Park, Kwang Seok Ahn, Hyun Jeong Kwak, Jae‐Young Um
The FASEB Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cajanolactone A, a Stilbenoid From Cajanus canjan (L.) Millsp, Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity via Suppressing Energy Intake
Zhuohui Luo, Jiawen Huang, Zhiping Li, Zhiwen Liu, Linchun Fu, Yingjie Hu, Xiaoling Shen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Zinc and the Innovative Zinc-α2-Glycoprotein Adipokine Play an Important Role in Lipid Metabolism: A Critical Review
Michalina Banaszak, Ilona Górna, Juliusz Przysławski
Nutrients.2021; 13(6): 2023. CrossRef - Natural products in the management of obesity: Fundamental mechanisms and pharmacotherapy
Yinghan Chan, Sin Wi Ng, Joycelin Zhu Xin Tan, Gaurav Gupta, Poonam Negi, Lakshmi Thangavelu, Sri Renukadevi Balusamy, Haribalan Perumalsamy, Wei Hsum Yap, Sachin Kumar Singh, Vanni Caruso, Kamal Dua, Dinesh Kumar Chellappan
South African Journal of Botany.2021; 143: 176. CrossRef - Group IIA secreted phospholipase A2 (PLA2G2A) augments adipose tissue thermogenesis
Michael S. Kuefner, Erin Stephenson, Mladen Savikj, Heather S. Smallwood, Qingming Dong, Christine Payré, Gérard Lambeau, Edwards A. Park
The FASEB Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - N-butylidenephthalide ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice and promotes browning through adrenergic response/AMPK activation in mouse beige adipocytes
Kang-Yun Lu, Kingsley Theras Primus Dass, Shinn-Zong Lin, Yu-Hua Tseng, Shih-Ping Liu, Horng-Jyh Harn
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids.2021; 1866(12): 159033. CrossRef - Green tea aqueous extract (GTAE) prevents high‐fat diet‐induced obesity by activating fat browning
Jie Li, Qiyang Chen, Xiuming Zhai, Dan Wang, Yujia Hou, Min Tang
Food Science & Nutrition.2021; 9(12): 6548. CrossRef - Ipragliflozin, an SGLT2 Inhibitor, Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Changes by Upregulating Energy Expenditure through Activation of the AMPK/ SIRT1 Pathway
Ji-Yeon Lee, Minyoung Lee, Ji Young Lee, Jaehyun Bae, Eugene Shin, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 921. CrossRef - The increase of uncoupling protein-1 expression after moderate intensity continuous exercises in obese females
Sugiharto, Banih Sakti Adji, Desiana Merawati, Adi Pranoto
Jurnal SPORTIF : Jurnal Penelitian Pembelajaran.2021; 7(2): 194. CrossRef - Effects of Royal Jelly and Tocotrienol Rich Fraction in obesity treatment of calorie-restricted obese rats: a focus on white fat browning properties and thermogenic capacity
Naimeh Mesri Alamdari, Pardis Irandoost, Neda Roshanravan, Mohammadreza Vafa, Mohammad Asghari Jafarabadi, Shahriar Alipour, Leila Roshangar, Mohammadreza Alivand, Farnaz Farsi, Farzad Shidfar
Nutrition & Metabolism.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Benefits of MicroRNA-22 Inhibition
Marc Thibonnier, Christine Esau
Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.2020; 30(2): 104. CrossRef - Grape pomace extract supplementation activates FNDC5/irisin in muscle and promotes white adipose browning in rats fed a high-fat diet
Cecilia Rodriguez Lanzi, Diahann J. Perdicaro, Julián Gambarte Tudela, Victoria Muscia, Ariel R. Fontana, Patricia I. Oteiza, Marcela A. Vazquez Prieto
Food & Function.2020; 11(2): 1537. CrossRef - Citrus aurantium L. polymethoxyflavones promote thermogenesis of brown and white adipose tissue in high-fat diet induced C57BL/6J mice
Guangning Kou, Yan Hu, Zixiao Jiang, Zhenqing Li, Peiyuan Li, Hongjie Song, Qiyang Chen, Zhiqin Zhou, Quanjun Lyu
Journal of Functional Foods.2020; 67: 103860. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of pomegranate peel extract treatment on anthropometry and body composition of overweight patients with diabetes mellitus type-2: A randomised clinical trial
Milkica Grabež, Ranko Škrbić, Miloš Stojiljković, Vesna Rudić-Grujić, Katarina Šavikin, Nebojša Menković, Gordana Zdunić, Nađa Vasiljević
Scripta Medica.2020; 51(1): 21. CrossRef - Milk fat globule membrane and its component phosphatidylcholine induce adipose browning both in vivo and in vitro
Tiange Li, Min Du, Hanning Wang, Xueying Mao
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2020; 81: 108372. CrossRef - Dynamic contrast‐enhanced MRI of brown and beige adipose tissues
Jadegoud Yaligar, Sanjay Kumar Verma, Venkatesh Gopalan, Rengaraj Anantharaj, Giang Thi Thu Le, Kavita Kaur, Karthik Mallilankaraman, MK Leow, SS Velan
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.2020; 84(1): 384. CrossRef - Taurine Stimulates Thermoregulatory Genes in Brown Fat Tissue and Muscle without an Influence on Inguinal White Fat Tissue in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mouse Model
Kyoung Soo Kim, Hari Madhuri Doss, Hee-Jin Kim, Hyung-In Yang
Foods.2020; 9(6): 688. CrossRef - White adipose tissue browning in critical illness: A review of the evidence, mechanisms and future perspectives
Elham Alipoor, Mohammad Javad Hosseinzadeh‐Attar, Mahsa Rezaei, Shima Jazayeri, Marianne Chapman
Obesity Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic and energetic benefits of microRNA-22 inhibition
Marc Thibonnier, Christine Esau, Sujoy Ghosh, Edward Wargent, Claire Stocker
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(1): e001478. CrossRef - Apple polyphenols induce browning of white adipose tissue
Yuki Tamura, Shigeto Tomiya, Junya Takegaki, Karina Kouzaki, Arata Tsutaki, Koichi Nakazato
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2020; 77: 108299. CrossRef - Adipose TBX1 regulates β-adrenergic sensitivity in subcutaneous adipose tissue and thermogenic capacity in vivo
Kathleen R. Markan, Lauren K. Boland, Abdul Qaadir King-McAlpin, Kristin E. Claflin, Michael P. Leaman, Morgan K. Kemerling, Madison M. Stonewall, Brad A. Amendt, James A. Ankrum, Matthew J. Potthoff
Molecular Metabolism.2020; 36: 100965. CrossRef - A systematic review of the association of neuregulin 4, a brown fat–enriched secreted factor, with obesity and related metabolic disturbances
Helda Tutunchi, Alireza Ostadrahimi, Mohammad‐Javad Hosseinzadeh‐Attar, Mahsa Miryan, Majid Mobasseri, Mehrangiz Ebrahimi‐Mameghani
Obesity Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Deficiency of glutathione peroxidase-1 and catalase attenuated diet-induced obesity and associated metabolic disorders
Hyung-Ran Kim, Eun-Jeong Choi, Jeong-Hae Kie, Joo-Ho Lee, Ju-Young Seoh
Acta Diabetologica.2020; 57(2): 151. CrossRef - Clinical Application Potential of Small Molecules that Induce Brown Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis by Improving Fat Metabolism
Kang-Yun Lu, Kingsley Theras Primus Dass, Sheng-Feng Tsai, Hong-Meng Chuang, Shinn-Zong Lin, Shih-Ping Liu, Horng-Jyh Harn
Cell Transplantation.2020; 29: 096368972092739. CrossRef - MiR‐92a regulates brown adipocytes differentiation, mitochondrial oxidative respiration, and heat generation by targeting SMAD7
Zhipin Zhang, Huixin Jiang, Xiang Li, Xiaomin Chen, Yihua Huang
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2020; 121(8-9): 3825. CrossRef - Bilirubin remodels murine white adipose tissue by reshaping mitochondrial activity and the coregulator profile of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor α
Darren M. Gordon, Kari L. Neifer, Abdul-Rizaq Ali Hamoud, Charles F. Hawk, Andrea L. Nestor-Kalinoski, Scott A. Miruzzi, Michael P. Morran, Samuel O. Adeosun, Jeffrey G. Sarver, Paul W. Erhardt, Robert E. McCullumsmith, David E. Stec, Terry D. Hinds
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2020; 295(29): 9804. CrossRef - The Presence of Active Brown Adipose Tissue Determines Cold-Induced Energy Expenditure and Oxylipin Profiles in Humans
Oana C Kulterer, Laura Niederstaetter, Carsten T Herz, Alexander R Haug, Andrea Bileck, Dietmar Pils, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Christopher Gerner, Florian W Kiefer
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(7): 2203. CrossRef - Downregulation of osteopontin inhibits browning of white adipose tissues through PI3K-AKT pathway in C57BL / 6 mice
Yi Lu, Yuhong Xu, Wanwan Yuan, Mengxi Wang, Yumeng Zhou, Kai Chen, Qiren Huang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2020; 866: 172822. CrossRef - Angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonism by losartan stimulates adipocyte browning via induction of apelin
Dong Young Kim, Mi Jin Choi, Tae Kyung Ko, Na Hyun Lee, Ok-Hee Kim, Hyae Gyeong Cheon
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2020; 295(44): 14878. CrossRef - Isoliquiritigenin Enhances the Beige Adipocyte Potential of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by JNK Inhibition
Hanbyeol Moon, Jung-Won Choi, Byeong-Wook Song, Il-Kwon Kim, Soyeon Lim, Seahyoung Lee, Ki-Chul Hwang, Sang Woo Kim
Molecules.2020; 25(23): 5660. CrossRef - In vitro evaluation of Hydrilla verticillata for anti-adipogenesis activity on 3T3 L1 cell lines
SPandi Prabha, S Sadhana, C Karthik, DG Caroline
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2020; 16(5): 498. CrossRef - Leptin Promotes White Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting the Hh Signaling Pathway
Jie Wang, Jing Ge, Haigang Cao, Xiaoyu Zhang, Yuan Guo, Xiao Li, Bo Xia, Gongshe Yang, Xin’e Shi
Cells.2019; 8(4): 372. CrossRef - Impact of Gut Microbiota on Host Glycemic Control
Céline Gérard, Hubert Vidal
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resveratrol on adipokines and myokines involved in fat browning: Perspectives in healthy weight against obesity
Oh Yoen Kim, Ji Yeon Chung, Juhyun Song
Pharmacological Research.2019; 148: 104411. CrossRef - A comprehensive diagnostic approach to detect underlying causes of obesity in adults
Eline S. van der Valk, Erica L.T. van den Akker, Mesut Savas, Lotte Kleinendorst, Jenny A. Visser, Mieke M. Van Haelst, Arya M. Sharma, Elisabeth F.C. van Rossum
Obesity Reviews.2019; 20(6): 795. CrossRef - Prostacyclin: A major prostaglandin in the regulation of adipose tissue development
Mohammad Sharifur Rahman
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(4): 3254. CrossRef - The expression of brown fat‐associated proteins in colorectal cancer and the relationship of uncoupling protein 1 with prognosis
Abdo Alnabulsi, Beatriz Cash, Yehfang Hu, Linda Silina, Ayham Alnabulsi, Graeme I. Murray
International Journal of Cancer.2019; 145(4): 1138. CrossRef - Garlic augments the functional and nutritional behavior of Doenjang, a traditional Korean fermented soybean paste
Ashutosh Bahuguna, Shruti Shukla, Jong Suk Lee, Vivek K. Bajpai, So-Young Kim, Yun Suk Huh, Young-Kyu Han, Myunghee Kim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Clomiphene promotes browning of white adipocytes via casein kinase-2 inhibition
Hyun-Jin Kim, Dong Young Kim, Hyae Gyeong Cheon
European Journal of Pharmacology.2019; 861: 172596. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine Regulation of Energy Metabolism Involving Different Types of Adipose Tissues
Qi Zhu, Bradley J. Glazier, Benjamin C. Hinkel, Jingyi Cao, Lin Liu, Chun Liang, Haifei Shi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(11): 2707. CrossRef - Tumor Cell “Slimming” Regulates Tumor Progression through PLCL1/UCP1‐Mediated Lipid Browning
Zhiyong Xiong, Wen Xiao, Lin Bao, Wei Xiong, Haibing Xiao, Yan Qu, Changfei Yuan, Hailong Ruan, Qi Cao, Keshan Wang, Zhengshuai Song, Cheng Wang, Wenjun Hu, Zeyuan Ru, Junwei Tong, Gong Cheng, Tianbo Xu, Xiangui Meng, Jian Shi, Zhixian Chen, Hongmei Yang,
Advanced Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Soyasaponin Ab alleviates postmenopausal obesity through browning of white adipose tissue
Han-Jun Kim, Eun-Ji Choi, Hyo Sung Kim, Chan-Woong Choi, Sik-Won Choi, Sun-Lim Kim, Woo-Duck Seo, Sun Hee Do
Journal of Functional Foods.2019; 57: 453. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Pomegranate Peel Extract and Probiotics on Pre-adipocyte Differentiation
Valeria Sorrenti, Cinzia Lucia Randazzo, Cinzia Caggia, Gabriele Ballistreri, Flora Valeria Romeo, Simona Fabroni, Nicolina Timpanaro, Marco Raffaele, Luca Vanella
Frontiers in Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Visfatin; a potential novel mediator of brown adipose tissue
Parmida Pourvali-Talatappeh, Elham Alipoor
Obesity Medicine.2019; 15: 100122. CrossRef - Strategies and methods for the correction of obesity and associated cardiovascular risk
T. Yu. Kuznetsova, M. A. Druzhilov, G. A. Chumakova, N. D. Veselovskaya
Russian Journal of Cardiology.2019; (4): 61. CrossRef - Polymeric Carriers for Controlled Drug Delivery in Obesity Treatment
Di Huang, Meng Deng, Shihuan Kuang
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 30(12): 974. CrossRef - Tbx15 is required for adipocyte browning induced by adrenergic signaling pathway
Wei Sun, Xuemei Zhao, Zhengqi Wang, Yi Chu, Liufeng Mao, Shaoqiang Lin, Xuefei Gao, Yuna Song, Xiaoyan Hui, Shiqi Jia, Shibing Tang, Yong Xu, Aimin Xu, Kerry Loomes, Cunchuan Wang, Donghai Wu, Tao Nie
Molecular Metabolism.2019; 28: 48. CrossRef - Effects of caloric restriction on the expression of lipocalin-2 and its receptor in the brown adipose tissue of high-fat diet-fed mice
Kyung-Ah Park, Zhen Jin, Hyeong Seok An, Jong Youl Lee, Eun Ae Jeong, Eun Bee Choi, Kyung Eun Kim, Hyun Joo Shin, Jung Eun Lee, Gu Seob Roh
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2019; 23(5): 335. CrossRef - Peripherally administered melanocortins induce mice fat browning and prevent obesity
Adriana R. Rodrigues, Maria J. Salazar, Sílvia Rocha-Rodrigues, Inês O. Gonçalves, Célia Cruz, Delminda Neves, Henrique Almeida, José Magalhães, Alexandra M. Gouveia
International Journal of Obesity.2019; 43(5): 1058. CrossRef - Chinese medicine Jinlida granules improve high-fat-diet induced metabolic disorders via activation of brown adipose tissue in mice
Hui Zhang, Yuanyuan Hao, Cong Wei, Bing Yao, Shen Liu, Hongru Zhou, Dan Huang, Chuanhai Zhang, Yiling Wu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2019; 114: 108781. CrossRef - Effects of lobeglitazone, a novel thiazolidinedione, on adipose tissue remodeling and brown and beige adipose tissue development in db/db mice
G Kim, Y-h Lee, M R Yun, J-Y Lee, E G Shin, B-W Lee, E S Kang, B-S Cha
International Journal of Obesity.2018; 42(3): 542. CrossRef - Air Pollution Has a Significant Negative Impact on Intentional Efforts to Lose Weight: A Global Scale Analysis
Morena Ustulin, So Young Park, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Jeong-taek Woo, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 320. CrossRef - Phytol stimulates the browning of white adipocytes through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) α in mice fed high-fat diet
Fenglin Zhang, Wei Ai, Xiaoquan Hu, Yingying Meng, Cong Yuan, Han Su, Lina Wang, Xiaotong Zhu, Ping Gao, Gang Shu, Qingyan Jiang, Songbo Wang
Food & Function.2018; 9(4): 2043. CrossRef - Nobiletin induces brown adipocyte-like phenotype and ameliorates stress in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Jameel Lone, Hilal Ahmad Parray, Jong Won Yun
Biochimie.2018; 146: 97. CrossRef - Regular aerobic exercise correlates with reduced anxiety and incresed levels of irisin in brain and white adipose tissue
Nazan Uysal, Oguz Yuksel, Servet Kizildag, Zeynep Yuce, Hikmet Gumus, Aslı Karakilic, Guven Guvendi, Basar Koc, Sevim Kandis, Mehmet Ates
Neuroscience Letters.2018; 676: 92. CrossRef - The Root of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidzumi Prevents Obesity and Glucose Intolerance and Increases Energy Metabolism in Mice
Mi Song, Soo-Kyoung Lim, Jing-Hua Wang, Hojun Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(1): 278. CrossRef - Differential actions of PPAR-α and PPAR-β/δ on beige adipocyte formation: A study in the subcutaneous white adipose tissue of obese male mice
Tamiris Lima Rachid, Flavia Maria Silva-Veiga, Francielle Graus-Nunes, Isabele Bringhenti, Carlos Alberto Mandarim-de-Lacerda, Vanessa Souza-Mello, Nobuyuki Takahashi
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(1): e0191365. CrossRef - Coordination Among Lipid Droplets, Peroxisomes, and Mitochondria Regulates Energy Expenditure Through the CIDE-ATGL-PPARα Pathway in Adipocytes
Linkang Zhou, Miao Yu, Muhammad Arshad, Wenmin Wang, Ye Lu, Jingyi Gong, Yangnan Gu, Peng Li, Li Xu
Diabetes.2018; 67(10): 1935. CrossRef - Lithocholic Acid Improves the Survival of Drosophila Melanogaster
Stefanie Staats, Gerald Rimbach, Axel Kuenstner, Simon Graspeuntner, Jan Rupp, Hauke Busch, Christian Sina, Ignacio R. Ipharraguerre, Anika E. Wagner
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Preconditioning lessens high fat induced metabolic syndrome along with markers of increased metabolic capacity in muscle and adipose tissue
Songpei Li, Xiu Zhou, Eunjung Jo, Ali Mahzari, Sherouk Fouda, Dongli Li, Kun Zhang, Ji-Ming Ye
Bioscience Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Alternative mRNA Splicing in the Pathogenesis of Obesity
Chi-Ming Wong, Lu Xu, Mabel Yau
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(2): 632. CrossRef - Krüppel-Like Factors
Nina M. Pollak, Matthew Hoffman, Ira J. Goldberg, Konstantinos Drosatos
JACC: Basic to Translational Science.2018; 3(1): 132. CrossRef - Dietary n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids upregulate energy dissipating metabolic pathways conveying anti-obesogenic effects in mice
Stefanie Worsch, Mathias Heikenwalder, Hans Hauner, Bernhard L. Bader
Nutrition & Metabolism.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of Capsaicin and Hesperidin Reduces the Effectiveness of Each Compound To Decrease the Adipocyte Size and To Induce Browning Features in Adipose Tissue of Western Diet Fed Rats
Andrea Mosqueda-Solís, Juana Sánchez, María P. Portillo, Andreu Palou, Catalina Picó
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2018; 66(37): 9679. CrossRef - Regulation of Adipose Tissue Metabolism by the Endocannabinoid System
Robin van Eenige, Mario van der Stelt, Patrick C.N. Rensen, Sander Kooijman
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2018; 29(5): 326. CrossRef - Cardiovascular and Metabolic Heterogeneity of Obesity
Ian J. Neeland, Paul Poirier, Jean-Pierre Després
Circulation.2018; 137(13): 1391. CrossRef - Zinc alpha2 glycoprotein promotes browning in adipocytes
Xin-Hua Xiao, Xiao-Yan Qi, Ya-Di Wang, Li Ran, Jing Yang, Huan-Li Zhang, Can-Xin Xu, Ge-Bo Wen, Jiang-Hua Liu
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 496(2): 287. CrossRef - Impacts of High Sodium Intake on Obesity-related Gene Expression
Minjee Lee, Miyoung Park, Juhee Kim, Soyoung Sung, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2018; 28(5): 364. CrossRef - Programming mediated by fatty acids affects uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) in brown adipose tissue
Perla P. Argentato, Helena de Cássia César, Débora Estadella, Luciana P. Pisani
British Journal of Nutrition.2018; 120(6): 619. CrossRef - Reversal of Fatty Infiltration After Suprascapular Nerve Compression Release Is Dependent on UCP1 Expression in Mice
Zili Wang, Brian T. Feeley, Hubert T. Kim, Xuhui Liu
Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research.2018; 476(8): 1665. CrossRef - Increase in relative skeletal muscle mass over time and its inverse association with metabolic syndrome development: a 7-year retrospective cohort study
Gyuri Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, You-Bin Lee, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Myricetin-induced brown adipose tissue activation prevents obesity and insulin resistance in db/db mice
Tao Hu, Xiaoxue Yuan, Gang Wei, Haoshu Luo, Hyuek Jong Lee, Wanzhu Jin
European Journal of Nutrition.2018; 57(1): 391. CrossRef - Effects of growth hormone on uncoupling protein 1 in white adipose tissues in obese mice
Misa Hayashi, Kumi Futawaka, Rie Koyama, Yue Fan, Midori Matsushita, Asuka Hirao, Yuki Fukuda, Ayako Nushida, Syoko Nezu, Tetsuya Tagami, Kenji Moriyama
Growth Hormone & IGF Research.2017; 37: 31. CrossRef - Position paper of the European Society of Cardiology–working group of coronary pathophysiology and microcirculation: obesity and heart disease
Lina Badimon, Raffaele Bugiardini, Edina Cenko, Judit Cubedo, Maria Dorobantu, Dirk J. Duncker, Ramón Estruch, Davor Milicic, Dimitris Tousoulis, Zorana Vasiljevic, Gemma Vilahur, Cor de Wit, Akos Koller
European Heart Journal.2017; 38(25): 1951. CrossRef - Browning of Abdominal Aorta Perivascular Adipose Tissue Inhibits Adipose Tissue Inflammation
Run-Mei Li, Sui-Qing Chen, Ning-Xi Zeng, Shu-Hui Zheng, Li Guan, Hai-Mei Liu, Le-Quan Zhou, Jin-Wen Xu
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2017; 15(9): 450. CrossRef - The role of adipose tissue in cancer-associated cachexia
Janina A Vaitkus, Francesco S Celi
Experimental Biology and Medicine.2017; 242(5): 473. CrossRef - Hormonal factors in the control of the browning of white adipose tissue
Jiamiao Hu, Mark Christian
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - European contribution to the study of ROS: A summary of the findings and prospects for the future from the COST action BM1203 (EU-ROS)
Javier Egea, Isabel Fabregat, Yves M. Frapart, Pietro Ghezzi, Agnes Görlach, Thomas Kietzmann, Kateryna Kubaichuk, Ulla G. Knaus, Manuela G. Lopez, Gloria Olaso-Gonzalez, Andreas Petry, Rainer Schulz, Jose Vina, Paul Winyard, Kahina Abbas, Opeyemi S. Adem
Redox Biology.2017; 13: 94. CrossRef - Resveratrol enhances brown adipocyte formation and function by activating AMP‐activated protein kinase (AMPK) α1 in mice fed high‐fat diet
Songbo Wang, Xingwei Liang, Qiyuan Yang, Xing Fu, Meijun Zhu, B. D. Rodgers, Qingyan Jiang, Michael V. Dodson, Min Du
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipoz doku ve enerji metabolizması üzerine etkileri
Meltem Mermer, Nilüfer Acar TEK
SDÜ Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Physiological roles of macrophages
Siamon Gordon, Luisa Martinez-Pomares
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology.2017; 469(3-4): 365. CrossRef - Brown Adipose Tissue Bioenergetics: A New Methodological Approach
María Calderon‐Dominguez, Martín Alcalá, David Sebastián, Antonio Zorzano, Marta Viana, Dolors Serra, Laura Herrero
Advanced Science.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Honokiol exerts dual effects on browning and apoptosis of adipocytes
Jameel Lone, Jong Won Yun
Pharmacological Reports.2017; 69(6): 1357. CrossRef - The Mixed Herbal Extract, CAPA, Prevents Obesity and Glucose Intolerance in Obese Mice
Miyoung Song
Journal of Korean Medicine for Obesity Research.2017; 17(2): 119. CrossRef - Brown Adipose Tissue: an Update on Recent Findings
Kara L. Marlatt, Eric Ravussin
Current Obesity Reports.2017; 6(4): 389. CrossRef - Radix Stellariae extract prevents high-fat-diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice by accelerating energy metabolism
Yin Li, Xin Liu, Yu Fan, Baican Yang, Cheng Huang
PeerJ.2017; 5: e3305. CrossRef - Adipocyte arrestin domain-containing 3 protein (Arrdc3) regulates uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) expression in white adipose independently of canonical changes in β-adrenergic receptor signaling
Shannon H. Carroll, Ellen Zhang, Bing F. Wang, Katherine B. LeClair, Arifeen Rahman, David E. Cohen, Jorge Plutzky, Parth Patwari, Richard T. Lee, Makoto Kanzaki
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(3): e0173823. CrossRef - Effect of Long-Term Green Tea Extract Supplementation on Peripheral Blood Leukocytes in CrossFit-Trained and Untrained Men
Agata Żak, Ilona Pokora
Central European Journal of Sport Sciences and Medicine.2017; 19: 67. CrossRef - Rapid modulation of lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice induced by eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipid from Cucumaria frondosa
Lingyu Zhang, Dan Wang, Min Wen, Lei Du, Changhu Xue, Jingfeng Wang, Jie Xu, Yuming Wang
Journal of Functional Foods.2017; 28: 28. CrossRef - Egr1 deficiency induces browning of inguinal subcutaneous white adipose tissue in mice
Cécile Milet, Marianne Bléher, Kassandra Allbright, Mickael Orgeur, Fanny Coulpier, Delphine Duprez, Emmanuelle Havis
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Purinergic Receptors in Adipose Tissue As Potential Targets in Metabolic Disorders
Marco Tozzi, Ivana Novak
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Phyllodulcin, a Natural Sweetener, Regulates Obesity-Related Metabolic Changes and Fat Browning-Related Genes of Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Eunju Kim, Soo-Min Lim, Min-Soo Kim, Sang-Ho Yoo, Yuri Kim
Nutrients.2017; 9(10): 1049. CrossRef - Yogurt and Cardiometabolic Diseases: A Critical Review of Potential Mechanisms
Melissa Anne Fernandez, Shirin Panahi, Noémie Daniel, Angelo Tremblay, André Marette
Advances in Nutrition.2017; 8(6): 812. CrossRef - Système endocannabinoïde : effets sur le métabolisme glucidique, mais aussi lipidique
A.-L. Sberna, P. Degrace, B. Vergès
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2016; 10(5): 407. CrossRef - The Fat Side of the Endocannabinoid System: Role of Endocannabinoids in the Adipocyte
Isabelle Matias, Ilaria Belluomo, Daniela Cota
Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research.2016; 1(1): 176. CrossRef - Liraglutide suppresses obesity and induces brown fat-like phenotype via Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase mediated pathwayin vivoandin vitro
Endong Zhu, Yang Yang, Juanjuan Zhang, Yongmei Li, Chunjun Li, Liming Chen, Bei Sun
Oncotarget.2016; 7(49): 81077. CrossRef - NS5ATP6 modulates intracellular triglyceride content through FGF21 and independently of SIRT1 and SREBP1
Zhongshu Li, Shenghu Feng, Li Zhou, Shunai Liu, Jun Cheng
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2016; 475(1): 133. CrossRef - Novel device for male infertility screening with single-ball lens microscope and smartphone
Yoshitomo Kobori, Peter Pfanner, Gail S. Prins, Craig Niederberger
Fertility and Sterility.2016; 106(3): 574. CrossRef - An Intestinal Microbiota–Farnesoid X Receptor Axis Modulates Metabolic Disease
Frank J. Gonzalez, Changtao Jiang, Andrew D. Patterson
Gastroenterology.2016; 151(5): 845. CrossRef - Feast and famine: Adipose tissue adaptations for healthy aging
Daniele Lettieri Barbato, Katia Aquilano
Ageing Research Reviews.2016; 28: 85. CrossRef - Hypothalamus and thermogenesis: Heating the BAT, browning the WAT
Cristina Contreras, Rubén Nogueiras, Carlos Diéguez, Gema Medina-Gómez, Miguel López
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 438: 107. CrossRef - Concomitant beige adipocyte differentiation upon induction of mesenchymal stem cells into brown adipocytes
Yung-Li Wang, Shih-Pei Lin, Patrick C.H. Hsieh, Shih-Chieh Hung
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2016; 478(2): 689. CrossRef
- Modulation of angiogenic switch in reprogramming browning and lipid metabolism in white adipocytes
- R1467H Variants of Rho Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor 11 (
ARHGEF11 ) are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Koreans - Qing Song Jin, So Hun Kim, Shan-Ji Piao, Hyun Ae Lim, Seung Youn Lee, Seong Bin Hong, Yong Seong Kim, Hun-Jae Lee, Moonsuk Nam
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(6):368-373. Published online December 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.6.368
- 4,131 View
- 23 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The human Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11 (
ARHGEF11 ) functions as an activator of Rho GTPases and is thought to influence insulin signaling. The R1467H variant ofARHGEF11 has been reported to be associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Western populations.Methods We investigated the effects of the R1467H variant on susceptibility to T2DM as well as related traits in a Korean population. We genotyped the R1467H (rs945508) of
ARHGEF11 in 689 unrelated T2DM patients and 249 non-diabetic individuals and compared the clinical and biochemical characteristics according to different alleles.Results The H allele was significantly more frequent in T2DM cases than in controls (
P = 0.037, 17.1% and 13.1%; respectively). H homozygocity was associated with a higher risk of T2DM compared to those with R/R or R/H genotype (odds ratio, 5.24; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 25.83;P = 0.042). The fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, fasting insulin, HOMA2-IR and HOMA2-%β levels did not differ significantly between different genotypes.Conclusion Our study replicated associations of the
ARHGEF11 polymorphism with increased risk of T2DM in a Korean population and thus supports previous data implicating a potential role ofARHGEF11 in the etiology of T2DM. Further studies revealing the underlying mechanism for this association are needed.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epigenetic alteration of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange Factor 11 (ARHGEF11) in cord blood samples in macrosomia exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia
Jie Yan, Rina Su, Wanyi Zhang, Yumei Wei, Chen Wang, Li Lin, Hui Feng, Huixia Yang
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2021; 34(3): 422. CrossRef -
Loss of
Arhgef11
in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Protects Against Hypertension-Induced Renal Injury
Ashley C. Johnson, Wenjie Wu, Esinam M. Attipoe, Jennifer M. Sasser, Erin B. Taylor, Kurt C. Showmaker, Patrick B. Kyle, Merry L. Lindsey, Michael R. Garrett
Hypertension.2020; 75(4): 1012. CrossRef - Transgenerational Obesity and Alteration of ARHGEF11 in the Rat Liver Induced by Intrauterine Hyperglycemia
Wanyi Zhang, Rina Su, Hui Feng, Li Lin, Chen Wang, Huixia Yang
Journal of Diabetes Research.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - ARHGEF11 affecting the placental insulin signaling pathway in fetal macrosomia of normal glucose tolerance pregnant women
Wanyi Zhang, Rina Su, Li Lin, Huixia Yang
Placenta.2018; 63: 7. CrossRef - Genetic variants and clinical relevance associated with gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese women: a case-control study
Jie Yan, Rina Su, Deng Ao, Yan Wang, Haijun Wang, Huixia Yang
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2018; 31(16): 2115. CrossRef - Human Rho Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor 11 (ARHGEF11) Regulates Dendritic Morphogenesis
Yutaka Mizuki, Manabu Takaki, Shinji Sakamoto, Sojiro Okamoto, Makiko Kishimoto, Yuko Okahisa, Masahiko Itoh, Norihito Yamada
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 18(1): 67. CrossRef - Allelic Variants in Arhgef11 via the Rho-Rock Pathway Are Linked to Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Contributes to Kidney Injury in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat
Zhen Jia, Ashley C. Johnson, Xuexiang Wang, Zibiao Guo, Albert W. Dreisbach, Jack R. Lewin, Patrick B. Kyle, Michael R. Garrett, Maria Pia Rastaldi
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(7): e0132553. CrossRef - The Rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor PDZ-RhoGEF governs susceptibility to diet-induced obesity and type 2 diabetes
Ying-Ju Chang, Scott Pownall, Thomas E Jensen, Samar Mouaaz, Warren Foltz, Lily Zhou, Nicole Liadis, Minna Woo, Zhenyue Hao, Previn Dutt, Philip J Bilan, Amira Klip, Tak Mak, Vuk Stambolic
eLife.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11 gene is associated with schizophrenia in a Japanese population
Yutaka Mizuki, Manabu Takaki, Yuko Okahisa, Shinji Sakamoto, Masafumi Kodama, Hiroshi Ujike, Yosuke Uchitomi
Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental.2014; 29(6): 552. CrossRef - Small G proteins and their regulators in cellular signalling
Roland Csépányi-Kömi, Magdolna Lévay, Erzsébet Ligeti
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2012; 353(1-2): 10. CrossRef - The Duration of Sulfonylurea Treatment Is Associated withβ-Cell Dysfunction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mi-Seon Shin, Jee Hee Yu, Chang Hee Jung, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2012; 14(11): 1033. CrossRef
- Epigenetic alteration of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange Factor 11 (ARHGEF11) in cord blood samples in macrosomia exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia
- Development and Validation of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire to Assess Diets of Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Seongbin Hong, Yunjin Choi, Hun-Jae Lee, So Hun Kim, Younju Oe, Seung Youn Lee, Moonsuk Nam, Yong Seong Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(1):32-39. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.32
- 4,757 View
- 64 Download
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Our aim was to assess the validity of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) by comparison with the 3-day diet record (DR) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods Eighty five type 2 diabetic patients (aged 33 to 70 years) from the Korean National Diabetes Program (KNDP) completed 3-day DR and FFQ. The FFQ was designed to reflect the eating pattern of Korean type 2 diabetic patients, and was based on the 2003 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The FFQ consists of 85 food items and 12 food groups. The validity of FFQ was assessed by comparison with the 3-day DR.
Results The mean age was 49 ± 10 years. Clinical characteristic including body weight, diabetic duration, and HbA1c were not different from the total cohort subjects (
n = 1,478). There were no significant differences in the mean intake of protein, fat and calcium estimated by the FFQ and the 3-day DR. Energy and carbohydrate estimated by the FFQ were higher than those estimated by the 3-day DR. The correlation coefficient was highest for energy (r = 0.740;P < 0.00) and lowest for iron (r = 0.269;P < 0.05). The Kappa values for energy, carbohydrate, protein, fat and calcium were 0.54, 0.37, 0.36, 0.46, and 0.19, respectively.Conclusion The FFQ is a reasonable instrument for assessing the intake of most macronutrients in Korean type 2 diabetes, although careful consideration is required for the food groups and nutrients for which the FFQ had low validity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire to Estimate Macronutrient Intake among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Malaysia
Norizzati Amsah, Zaleha Md Isa, Norfazilah Ahmad
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 506. CrossRef - Development of a Semi-Quantitative Food-Frequency Questionnaire for Korean Adults with Obesity
Jina Chung, Seoeun Ahn, Hyojee Joung, Sangah Shin
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4848. CrossRef - Development of semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire for obese Korean adults
S.H. Kim, J. Chung, S. Ahn, H. Joung
Proceedings of the Nutrition Society.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Construct validity of the Suboptimal Health Status Questionnaire-25 in a Ghanaian population
Eric Adua, Ebenezer Afrifa-Yamoah, Kwasi Frimpong, Esther Adama, Shantha P. Karthigesu, Enoch Odame Anto, Emmanuel Aboagye, Yuxiang Yan, Youxin Wang, Xuerui Tan, Wei Wang
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutritional Status Measurement Instruments for Diabetes: A Systematic Psychometric Review
Pedro Montagut-Martínez, David Pérez-Cruzado, José Joaquín García-Arenas
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(16): 5719. CrossRef - Nutrition Status Among HIV‐Positive and HIV‐Negative Inpatients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Tássia Kirchmann Lazzari, Gabriele Carra Forte, Denise Rossato Silva
Nutrition in Clinical Practice.2018; 33(6): 858. CrossRef - Identifying Dietary Patterns Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment in Older Korean Adults Using Reduced Rank Regression
Dayeon Shin, Kyung Lee, Mi-Hye Kim, Hung Kim, Yun An, Hae-Kyung Chung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2018; 15(1): 100. CrossRef - Development and relative validity of semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire for Korean adults
Sohye Kim, Jung Sug Lee, Kyung Hee Hong, Hye Sun Yeom, Yeon Seo Nam, Ju Young Kim, Yoo Kyung Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2018; 51(1): 103. CrossRef - Reproducibility and validity of an FFQ developed for the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
Dong Woo Kim, Sujin Song, Jung Eun Lee, Kyungwon Oh, Jeeseon Shim, Sanghui Kweon, Hee Young Paik, Hyojee Joung
Public Health Nutrition.2015; 18(8): 1369. CrossRef - Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies
Jee-Seon Shim, Kyungwon Oh, Hyeon Chang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2014; 36: e2014009. CrossRef - Validity and reproducibility of an interviewer-administered food frequency questionnaire in Austrian adults at risk of or with overt diabetes mellitus
Michaela Farukuoye, Klaus Strassburger, Gertrud Kacerovsky-Bielesz, Guido Giani, Michael Roden
Nutrition Research.2014; 34(5): 410. CrossRef - Reproducibility and validity of a quantitative FFQ designed for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from southern Brazil
Roberta Aguiar Sarmento, Juliana Peçanha Antonio, Bárbara Pelicioli Riboldi, Karina Romeu Montenegro, Rogério Friedman, Mirela Jobim de Azevedo, Jussara Carnevale de Almeida
Public Health Nutrition.2014; 17(10): 2237. CrossRef - Instant Noodle Intake and Dietary Patterns Are Associated with Distinct Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Korea
Hyun Joon Shin, Eunyoung Cho, Hae-Jeung Lee, Teresa T. Fung, Eric Rimm, Bernard Rosner, JoAnn E. Manson, Kevin Wheelan, Frank B. Hu
The Journal of Nutrition.2014; 144(8): 1247. CrossRef - Relative validity of an FFQ to estimate daily food and nutrient intakes for Chilean adults
Mahshid Dehghan, Solange Martinez, Xiaohe Zhang, Pamela Seron, Fernando Lanas, Shofiqul Islam, Anwar T Merchant
Public Health Nutrition.2013; 16(10): 1782. CrossRef - Development of a quantitative food frequency questionnaire for Brazilian patients with type 2 diabetes
Roberta Aguiar Sarmento, Bárbara Pelicioli Riboldi, Ticiana da Costa Rodrigues, Mirela Jobim de Azevedo, Jussara Carnevale de Almeida
BMC Public Health.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Breast Arterial Calcifications, Metabolic Syndrome, and the 10-Year Coronary Heart Disease Risk: A Cross-Sectional Case-Control Study
Mi Jin Bae, Sang Yeoup Lee, Yun Jin Kim, Jeong Gyu Lee, Dong Wook Jeong, Yu Hyeon Yi, Young Hye Cho, Eun Jung Choi, Ki Seok Choo
Journal of Women's Health.2013; 22(7): 625. CrossRef - Development and validation of a quantitative food frequency questionnaire to assess nutritional status in Korean adults
Youn Ju Na, Seon Heui Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2012; 6(5): 444. CrossRef - Relations of nutritional intake to age, sex and body mass index in Japanese elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: The Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial
Yukio Yoshimura, Chiemi Kamada, Keiko Takahashi, Tae Kaimoto, Satoshi Iimuro, Yasuo Ohashi, Atsushi Araki, Hiroyuki Umegaki, Takashi Sakurai, Hideki Ito
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2012; 12(s1): 29. CrossRef - Validation Study of a Dietary Questionnaire for Assessing Exposure to Food-Borne Hazards
Hyemi Kim, Seul Ki Choi, Sangah Shin, Kyung Youn Lee, Sanghee Shin, Jung Won Lee, Soo Hyun Yu, Hye-Soen Nam, Mi-Gyeong Kim, Hyojee Joung
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2011; 44(2): 171. CrossRef
- Development of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire to Estimate Macronutrient Intake among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Malaysia
- Direct Medical Costs of Type 2 Diabetic Patients in the Tertiary Hospital.
- Joo An Hwang, Tae Chin Park, Sun Hye Jung, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, So Hun Kim, Moon Suk Nam, Tae Hyun Kim, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwan Woo Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(3):259-268. Published online June 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.3.259
- 2,210 View
- 31 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a common, chronic and costly disease. Its prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide. Diabetes has big economic burden mainly because of its chronic complications. We analyzed the annual direct medical costs of type 2 diabetic patients, including the costs associated with its complications in Korea retrospectively. METHODS: We enrolled 531 type 2 diabetic patients who had been treated in the 3 Tertiary Hospital in 2005. Clinical characteristics, duration of diabetes, modality of glycemic control, and presence of microvascular and macrovascular complications were assessed by the review of medical records. The annual direct medical costs were assessed using the hospital electronic database and included insurance covered and uncovered medical costs. RESULTS: The annual direct medical costs of type 2 diabetic patients without any complications was 1,184,563 won (95% CI for mean: 973,006~1,396,121 won). Compared to diabetic patients without complications, annual total medical costs increased 4.7-fold, 10.7-fold, and 8.8-fold in patients with microvascular complications, macrovascular complications and both complications, respectively. Hospitalization costs largely increased by 78.7-fold and 61.0-fold in patients with macrovascular complications and both complications, respectively. Major complications to increase medical costs were kidney transplantation (23.1-fold), dialysis (21.0-fold), PTCA or CABG (12.4-fold), and leg amputation (11.8-fold). The total medical costs dramatically increased according to the stage of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy. CONCLUSION: Diabetic complications have a substantial impact on the direct medical costs of type 2 diabetic patients. The prevention of diabetic complications will benefit the patients as well as the overall healthcare expenditures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Policy Proposals for Infection Control in Patients with Chronic Wounds
Kyung-Chul Moon, Donghyeok Shin, Kyu-Won Baek, Changsik John Pak, Young-Joon Jun
Journal of Wound Management and Research.2022; 18(3): 249. CrossRef - Effects of Co‐administration of Sulfonylureas and Antimicrobial Drugs on Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Using a Case‐Crossover Design
Sera Lee, Miyoung Ock, Hun‐Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim
Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy.2020; 40(9): 902. CrossRef - The effect of continuity of care on the incidence of end-stage renal disease in patients with newly detected type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a retrospective cohort study
Yun Jung Jang, Yoon Soo Choy, Chung Mo Nam, Ki Tae Moon, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Nephrology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Social Welfare Information for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Jea Yeon Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(2): 117. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia and Health Costs
Yong-ho Lee, Gyuri Kim, Eun Seok Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(1): 11. CrossRef - Outcome Research in Diabetes
Kwan Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(1): 2. CrossRef - Costs of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Kwan Woo Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 567. CrossRef - How Much Amount of Socioeconomic Loss Is Caused by Digestive Diseases?
Kyung Sik Park
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2011; 58(6): 297. CrossRef
- Policy Proposals for Infection Control in Patients with Chronic Wounds
- Effects of Walking and Physical Activity on Glucose Regulation among Type 2 Diabetics.
- Yoonsuk Jekal, Mi Kyung Lee, Eun Sung Kim, Ji Hye Park, Hyun Ji Lee, Seung Jin Han, Eun Seok Kang, Hyun Chul Lee, So Hun Kim, Justin Y Jeon
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(1):60-67. Published online February 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.1.60
- 2,198 View
- 37 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Physical activity, especially walking is strongly recommended to control blood glucose among type 2 diabetic patients. Furthermore, physical activity is one of the most important tools to prevent secondary diabetes complications among type 2 diabetic patients such as retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy etc. The purpose of the study was to examine the association between the level of walking and physical activity and glucose control among Korean adults with type 2 diabetes. METHODS: A total of 250 patients with type 2 diabetes (98 males and 152 females) were recruited (mean age = 62.1 +/- 10.2 years) in the current study. The height, weight, waist and hip circumference were measured, and the level of physical activity and total walking hour were measured by physical activity scale for elderly (PASE). High density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), total cholesterol, triglyceride, fasting glucose and oral glucose tolerance test, creatinine, uric acid, total protein, albumin, hemoglobin A1c were measured. RESULTS: After adjusting for potential covariates such as age, education, occupation income, smoking, and drinking, male patients who spent least time in walking were more likely to have 2 hour serum glucose level in oral glucose tolerance above 200 mg/dL than counterparts who spent most time in walking with age adjusted (Relative Risk (RR) = 11.75, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) = 1.94-71.00). Male patients who were in the least active group were 5.92 time (95% CI = 1.39-25.28) more likely to have 2 hour serum glucose level in oral glucose tolerance over 200 mg/dL than counterparts in the most active group. However, there was no significant finding in females. CONCLUSIONS: The current study showed that physical activity and walking are effective method to maintain glucose tolerance among type 2 diabetic male patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 호남권 지역주민의 건강행태와 만성질환 관리현황
선아 김, 정은 이
Public Health Weekly Report.2024; 17(2): 46. CrossRef - A Study Analyzing the Relationship among Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG), Obesity Index, Physical Activity, and Beverage and Alcohol Consumption Frequency in 20s and 30s:The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2013-2015
Yujin Lee, Jung-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 19. CrossRef - Travel Guidance for People with Diabetes
Izadi Morteza, Hosseini Mahboobeh Sadat, Pazham Hossein
International Journal of Travel Medicine and Global Health.2015; 3(4): 149. CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes According to Gender among Korean Employees
Sang-A Kim, Woong-Sub Park, Su Jeong Yu, Young Ran Chae, Donghee Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7589. CrossRef - Low Levels of Physical Activity Are Associated with Increased Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors in Korean Adults
Dong Hoon Lee, Yoon Myung Kim, Yoonsuk Jekal, Sukyung Park, Kyong-Chol Kim, Masayo Naruse, Sun Hyun Kim, Sang-Hwan Kim, Ji-Hye Park, Mi Kyung Lee, Sang Hui Chu, Justin Y. Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 132. CrossRef - Association between Obesity and Physical Fitness, and Hemoglobin A1c Level and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults
Yoonsuk Jekal, Mi-Kyung Lee, Sukyung Park, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jun-Young Kim, Jung-Ui Kang, Masayo Naruse, Sang-Hwan Kim, Sun-Hyeon Kim, Sang Hui Chu, Sang-Hoon Suh, Justin Y Jeon
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(3): 182. CrossRef
- 호남권 지역주민의 건강행태와 만성질환 관리현황
- A Case of Insulinoma Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Sung Soo Yoo, Wan Sub Shim, Chul Hyun Kim, Ki Cheol Ha, Seung Min Lye, Eun Joo Kim, So Hun Kim, Seong Bin Hong, Moonsuk Nam, Yong Seong Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(6):517-519. Published online November 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.6.517
- 2,036 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An insulinoma is an endocrine tumor of the pancreas derived from the beta cells with abnormal insulin secretion. An insulinoma is rare, the incidence being estimated at only four per one million person-years. The association of diabetes mellitus and insulinoma is extraordinarily rare, but we should not overlook an insulinoma as a possible cause of hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus. A 70-year-old diabetic man who had been treated with oral hypoglycemic agents for type 2 diabetes suffered from night sweating for 10 days. Even after he stopped taking his oral hypoglycemic agents, the night sweating continued. The patient was admitted to evaluate the cause of the recurrent hypoglycemic events. After a 72-hour fasting test and selective arterial calcium stimulation test with venous sampling, he was diagnosed with insulinoma accompanied by type 2 diabetes mellitus. In the course of the study, the patient was also incidentally diagnosed with lung cancer.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





